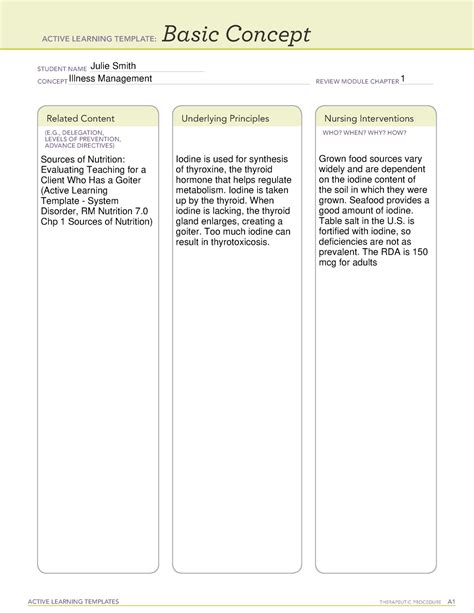
As a nursing student preparing for the Assessment Technologies Institute (ATI) exam, it's essential to have a solid understanding of nutrition concepts. Nutrition plays a critical role in maintaining optimal health, preventing diseases, and promoting recovery from illnesses. In this article, we'll delve into five essential nutrition concepts that will help you succeed on the ATI exam.
Proper nutrition is vital for overall health, and nurses must understand how to apply nutrition principles to promote patient well-being. The ATI exam assesses your knowledge of nutrition concepts, including nutrition assessment, planning, and implementation. By mastering these concepts, you'll be better equipped to provide high-quality patient care and pass the ATI exam with confidence.
Nutrition Assessment

Nutrition assessment is the process of evaluating a patient's nutritional status to identify potential nutrition-related problems. This involves collecting data on the patient's medical history, dietary habits, and lifestyle factors that may impact their nutritional status. As a nurse, you'll need to conduct a thorough nutrition assessment to develop an effective nutrition plan.
There are several tools and methods used in nutrition assessment, including:
- 24-hour dietary recall: This involves asking the patient to recall their food intake over the past 24 hours.
- Food frequency questionnaire: This is a questionnaire that asks the patient about their typical food intake over a specific period.
- Anthropometric measurements: This includes measuring the patient's height, weight, and body mass index (BMI).
Nutrition Assessment Techniques
Some common nutrition assessment techniques include:
- Physical examination: This involves assessing the patient's physical condition, including their weight, height, and body composition.
- Laboratory tests: This includes blood tests to assess the patient's nutritional status, such as complete blood count (CBC) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels.
- Dietary analysis: This involves analyzing the patient's dietary habits to identify potential nutritional deficiencies.
Nutrition Planning

Once you've conducted a thorough nutrition assessment, you'll need to develop a nutrition plan that addresses the patient's specific nutritional needs. Nutrition planning involves setting goals and objectives for the patient's nutrition care, as well as selecting appropriate nutrition interventions.
There are several steps involved in nutrition planning, including:
- Identifying nutrition-related problems: This involves analyzing the data collected during the nutrition assessment to identify potential nutrition-related problems.
- Setting nutrition goals: This involves developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the patient's nutrition care.
- Selecting nutrition interventions: This involves choosing appropriate nutrition interventions to address the patient's nutrition-related problems.
Nutrition Planning Strategies
Some common nutrition planning strategies include:
- Developing a personalized meal plan: This involves creating a meal plan that takes into account the patient's dietary needs, preferences, and lifestyle.
- Implementing nutrition education: This involves educating the patient on healthy eating habits and providing them with the necessary tools and resources to make informed food choices.
- Coordinating with other healthcare professionals: This involves working with other healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians and physicians, to ensure that the patient receives comprehensive nutrition care.
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats

Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the three main macronutrients that provide energy and support growth and maintenance of body tissues. Understanding the role of each macronutrient is essential for developing effective nutrition plans.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. They come in two forms: simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starches and fibers).
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing body tissues, including muscles, bones, and skin. They also play a critical role in producing enzymes, hormones, and other biomolecules.
- Fats: Fats are an essential source of energy and help absorb vitamins A, D, E, and K. They also play a critical role in maintaining healthy skin and hair.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential vitamins and minerals that play a critical role in maintaining optimal health. Some common micronutrients include:
- Vitamins: Vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and eyes, as well as supporting immune function.
- Minerals: Minerals are essential for maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles, as well as supporting nerve function.
Therapeutic Diets

Therapeutic diets are specialized diets designed to manage specific medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease. Understanding therapeutic diets is essential for developing effective nutrition plans that address the patient's specific nutritional needs.
Some common therapeutic diets include:
- Low-sodium diet: This diet is designed to manage hypertension and heart disease.
- Low-fat diet: This diet is designed to manage heart disease and obesity.
- Gluten-free diet: This diet is designed to manage celiac disease and gluten intolerance.
Therapeutic Diet Strategies
Some common therapeutic diet strategies include:
- Meal planning: This involves creating a meal plan that takes into account the patient's dietary needs and restrictions.
- Food selection: This involves selecting foods that are consistent with the patient's therapeutic diet.
- Nutrition education: This involves educating the patient on healthy eating habits and providing them with the necessary tools and resources to make informed food choices.
Nutrition Support

Nutrition support is essential for patients who are unable to meet their nutritional needs through oral intake. Nutrition support involves providing patients with the necessary nutrients to maintain optimal health.
Some common nutrition support strategies include:
- Enteral nutrition: This involves providing patients with nutrients through a feeding tube.
- Parenteral nutrition: This involves providing patients with nutrients through an intravenous (IV) line.
- Supplements: This involves providing patients with nutritional supplements to support their nutritional needs.
Nutrition Support Techniques
Some common nutrition support techniques include:
- Assessing the patient's nutritional status: This involves evaluating the patient's nutritional needs and developing a plan to address any nutritional deficiencies.
- Selecting nutrition support options: This involves choosing the most appropriate nutrition support option for the patient.
- Monitoring the patient's response to nutrition support: This involves closely monitoring the patient's response to nutrition support and making adjustments as needed.
In conclusion, mastering the essential nutrition concepts outlined in this article will help you succeed on the ATI exam and provide high-quality patient care. Remember to focus on nutrition assessment, planning, and implementation, as well as the role of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in maintaining optimal health. Additionally, understanding therapeutic diets and nutrition support strategies will help you develop effective nutrition plans that address the patient's specific nutritional needs.
Take the next step in your nursing career by mastering these essential nutrition concepts and providing high-quality patient care.
Gallery of Nutrition Concepts






FAQ Section
What is the importance of nutrition assessment in patient care?
+Nutrition assessment is essential in patient care as it helps identify potential nutrition-related problems and develop effective nutrition plans to address these problems.
What are the three main macronutrients that provide energy and support growth and maintenance of body tissues?
+The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What is the purpose of therapeutic diets in patient care?
+Therapeutic diets are designed to manage specific medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease, by providing patients with the necessary nutrients to maintain optimal health.