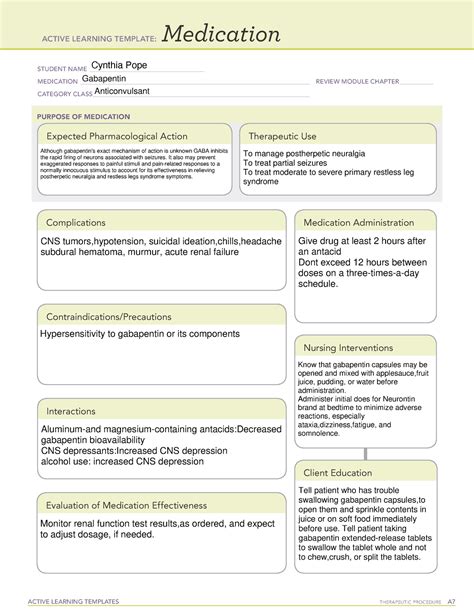
Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. It belongs to a class of medications known as anticonvulsants, which work by affecting the way that nerves send messages to your brain. In recent years, gabapentin has gained popularity as a treatment for various off-label uses, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and fibromyalgia. However, its effectiveness for these conditions is still a topic of debate among medical professionals.
What is Gabapentin Used For?
Gabapentin is primarily used to treat the following conditions:
- Partial seizures: Gabapentin is used in combination with other medications to treat partial seizures, which affect only one part of the brain.
- Nerve pain caused by shingles: Gabapentin is used to treat nerve pain caused by shingles, a condition characterized by a painful rash that usually appears on one side of the body.
- Diabetic neuropathy: Gabapentin is sometimes used to treat nerve pain caused by diabetes.
In addition to its FDA-approved uses, gabapentin is also prescribed off-label for various conditions, including:
- Anxiety disorders: Some studies suggest that gabapentin may be effective in reducing anxiety symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders.
- Insomnia: Gabapentin may help improve sleep quality in patients with insomnia.
- Fibromyalgia: Gabapentin may be used to treat chronic pain and fatigue associated with fibromyalgia.
How Does Gabapentin Work?
Gabapentin works by affecting the way that nerves send messages to your brain. It is thought to bind to certain receptors in the brain, which can help to reduce the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin also has a calming effect on the nervous system, which can help to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
Benefits of Gabapentin
Gabapentin has several benefits that make it a popular treatment option for various conditions. Some of the benefits of gabapentin include:
- Effective pain relief: Gabapentin is effective in reducing nerve pain caused by shingles and diabetic neuropathy.
- Anti-anxiety effects: Gabapentin may help to reduce anxiety symptoms in patients with anxiety disorders.
- Improved sleep: Gabapentin may help to improve sleep quality in patients with insomnia.
- Low risk of addiction: Unlike some other medications, gabapentin has a low risk of addiction and dependence.
Gabapentin Side Effects
While gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including:
- Dizziness and drowsiness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Swelling of the hands and feet
Gabapentin Dosage
The dosage of gabapentin varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient's individual needs. Here are some general guidelines for gabapentin dosage:
- Partial seizures: The recommended starting dose is 300-400 mg three times a day.
- Nerve pain caused by shingles: The recommended starting dose is 300-400 mg three times a day.
- Diabetic neuropathy: The recommended starting dose is 300-400 mg three times a day.
- Anxiety disorders: The recommended starting dose is 100-300 mg three times a day.
- Insomnia: The recommended starting dose is 100-300 mg at bedtime.
Gabapentin Interactions
Gabapentin can interact with other medications, including:
- Antacids: Antacids may reduce the absorption of gabapentin.
- Opioids: Gabapentin may increase the risk of respiratory depression when taken with opioids.
- Benzodiazepines: Gabapentin may increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression when taken with benzodiazepines.
Gabapentin Warnings and Precautions
Gabapentin can cause some serious side effects, including:
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors: Gabapentin may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in some patients.
- Respiratory depression: Gabapentin may increase the risk of respiratory depression when taken with other medications.
- Angioedema: Gabapentin may cause angioedema, a condition characterized by swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat.

Gabapentin Treatment Plan
A gabapentin treatment plan typically involves the following steps:
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Before starting gabapentin, consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the potential benefits and risks of the medication.
- Start with a low dose: Start with a low dose of gabapentin and gradually increase the dose as needed.
- Monitor side effects: Monitor side effects closely and report any concerns to a healthcare professional.
- Regular follow-up: Regular follow-up with a healthcare professional is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of gabapentin and adjust the dose as needed.





Conclusion
Gabapentin is a medication that is primarily used to treat partial seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. While it has several benefits, including effective pain relief and anti-anxiety effects, it can also cause some side effects. A gabapentin treatment plan typically involves starting with a low dose and gradually increasing the dose as needed. Regular follow-up with a healthcare professional is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of gabapentin and adjust the dose as needed.
What is gabapentin used for?
+Gabapentin is primarily used to treat partial seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. It is also used to treat various off-label conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and fibromyalgia.
How does gabapentin work?
+Gabapentin works by affecting the way that nerves send messages to your brain. It binds to certain receptors in the brain, which can help to reduce the transmission of pain signals.
What are the benefits of gabapentin?
+Gabapentin has several benefits, including effective pain relief, anti-anxiety effects, and improved sleep quality. It also has a low risk of addiction and dependence.