Heparin is a widely used medication that plays a crucial role in preventing and treating blood clots. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of the essential facts about heparin. In this article, we will delve into the world of heparin medication, exploring its uses, benefits, risks, and more.
Heparin is a complex medication that requires careful administration and monitoring. Whether you are a patient, a healthcare professional, or simply interested in learning more about this medication, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of heparin.

What is Heparin?
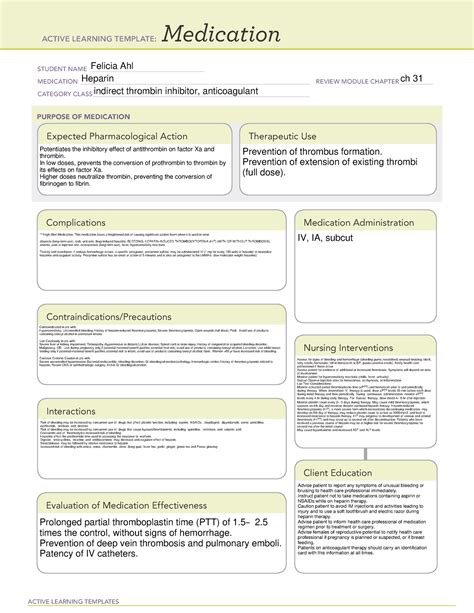
Heparin is an anticoagulant medication that is used to prevent and treat blood clots. It works by inhibiting the formation of blood clots and preventing the growth of existing clots. Heparin is commonly used to treat conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and atrial fibrillation.
Heparin is available in two forms: unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). UFH is the original form of heparin, while LMWH is a newer, more convenient form that has a longer half-life and can be administered subcutaneously.
How Does Heparin Work?
Heparin works by binding to antithrombin, a protein that inhibits the formation of blood clots. When heparin binds to antithrombin, it increases the protein's ability to inhibit the coagulation cascade, thereby preventing the formation of blood clots.
Heparin also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce the risk of complications associated with blood clots.

Benefits of Heparin
Heparin has several benefits that make it an essential medication in the prevention and treatment of blood clots. Some of the benefits of heparin include:
- Prevention of blood clots: Heparin is highly effective in preventing blood clots from forming, which can reduce the risk of complications such as DVT and PE.
- Treatment of blood clots: Heparin can also be used to treat existing blood clots, helping to reduce the risk of complications and promote healing.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Heparin has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce the risk of complications associated with blood clots.

Risks and Side Effects of Heparin
While heparin is a highly effective medication, it is not without risks and side effects. Some of the risks and side effects of heparin include:
- Bleeding: Heparin can increase the risk of bleeding, which can be a serious complication.
- Thrombocytopenia: Heparin can cause a decrease in platelet count, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term use of heparin can increase the risk of osteoporosis.

Administration and Monitoring of Heparin
Heparin requires careful administration and monitoring to ensure its safe and effective use. Some of the key considerations when administering and monitoring heparin include:
- Dosage: Heparin dosage should be carefully titrated to achieve the desired anticoagulant effect.
- Laboratory monitoring: Regular laboratory monitoring is essential to ensure that heparin is not causing adverse effects such as thrombocytopenia or osteoporosis.
- Patient education: Patients should be educated on the risks and benefits of heparin, as well as how to administer the medication safely and effectively.

Gallery of Heparin Medication






What is heparin used for?
+Heparin is used to prevent and treat blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
How does heparin work?
+Heparin works by binding to antithrombin, a protein that inhibits the formation of blood clots.
What are the risks and side effects of heparin?
+Heparin can increase the risk of bleeding, thrombocytopenia, and osteoporosis.
In conclusion, heparin is a highly effective medication that plays a crucial role in preventing and treating blood clots. While it is not without risks and side effects, careful administration and monitoring can help to minimize these risks. By understanding the benefits and risks of heparin, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to ensure its safe and effective use.