Metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as beta-blockers. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of metoprolol, exploring its uses, benefits, side effects, and interactions.
What is Metoprolol?

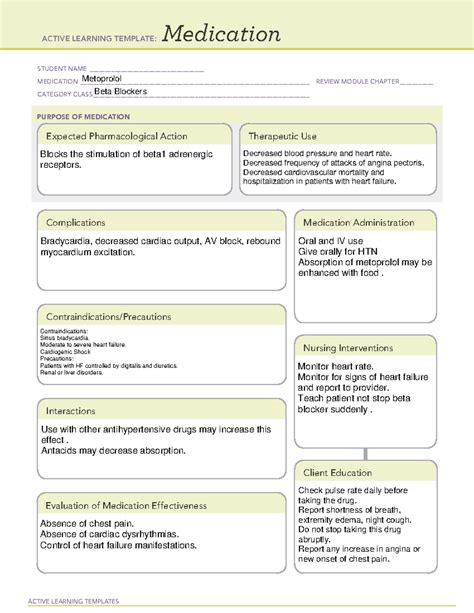
Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that works by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart's contractions. This decreases the amount of oxygen the heart needs, which in turn reduces the frequency of angina attacks. Additionally, metoprolol lowers blood pressure by reducing the resistance in the blood vessels.
Uses of Metoprolol
Metoprolol is used to treat a variety of conditions, including:
- High Blood Pressure: Metoprolol is often prescribed to treat high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Angina: Metoprolol helps to reduce the frequency and severity of angina attacks by decreasing the heart's oxygen demand.
- Heart Failure: Metoprolol is used to treat heart failure, a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
- Tachyarrhythmias: Metoprolol is used to treat irregular heartbeats, such as atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia.
Benefits of Metoprolol
The benefits of metoprolol include:
- Reduced Blood Pressure: Metoprolol helps to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Improved Heart Function: Metoprolol improves heart function by reducing the heart's workload and increasing the efficiency of the heart's contractions.
- Reduced Angina Frequency: Metoprolol reduces the frequency and severity of angina attacks, improving quality of life.
- Increased Survival: Metoprolol has been shown to increase survival in patients with heart failure and high blood pressure.
Side Effects of Metoprolol
Like all medications, metoprolol can cause side effects, including:
- Fatigue: Metoprolol can cause fatigue, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
- Shortness of Breath: Metoprolol can cause shortness of breath, especially in patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
- Cold Extremities: Metoprolol can cause cold hands and feet due to reduced blood flow.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Metoprolol can cause nausea and vomiting, especially when first starting the medication.
Interactions with Other Medications
Metoprolol can interact with other medications, including:
- Diuretics: Metoprolol can increase the risk of low blood pressure when taken with diuretics.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Metoprolol can increase the risk of low blood pressure and heart failure when taken with calcium channel blockers.
- Anti-Arrhythmics: Metoprolol can increase the risk of arrhythmias when taken with anti-arrhythmic medications.
How to Take Metoprolol
Metoprolol is typically taken orally, once or twice daily, depending on the condition being treated. It is essential to follow the doctor's instructions and take the medication as directed.
Gallery of Metoprolol Medication






Frequently Asked Questions
What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions.
What are the side effects of metoprolol?
+Common side effects of metoprolol include fatigue, shortness of breath, cold extremities, and nausea and vomiting.
Can I take metoprolol with other medications?
+Metoprolol can interact with other medications, including diuretics, calcium channel blockers, and anti-arrhythmics. It is essential to consult with a doctor before taking metoprolol with other medications.
In conclusion, metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication that offers numerous benefits for patients with high blood pressure, chest pain, and certain heart-related conditions. While it can cause side effects and interact with other medications, metoprolol remains a valuable treatment option for many patients. By understanding the uses, benefits, and potential risks of metoprolol, patients can work with their doctors to develop an effective treatment plan.