Morphine is a potent opioid analgesic commonly used to manage moderate to severe pain. When administered safely and correctly, morphine can be an effective tool for pain management. However, its potential for addiction and respiratory depression requires careful attention to dosing and administration. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on the safe administration of morphine medication, including its uses, side effects, and dosing considerations.
Understanding Morphine Medication

Morphine is a natural opioid derived from the opium poppy plant. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the perception of pain. Morphine is available in various formulations, including oral tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions, as well as injectable and epidural forms.
Uses of Morphine Medication
Morphine is commonly used to manage a range of pain conditions, including:
- Acute pain: Morphine is often used to manage acute pain in the hospital setting, such as post-operative pain or pain associated with trauma.
- Chronic pain: Morphine can be used to manage chronic pain conditions, such as cancer pain or neuropathic pain.
- Palliative care: Morphine is often used in palliative care to manage pain and symptoms in patients with advanced illnesses.
Safe Administration of Morphine Medication

To ensure safe administration of morphine medication, healthcare providers should follow these guidelines:
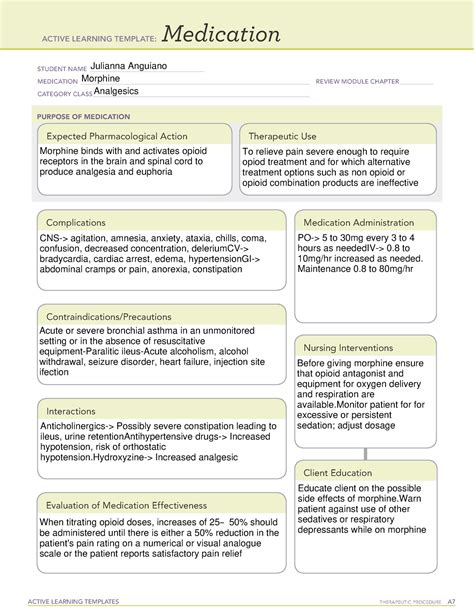
- Dosing: Morphine dosing should be individualized based on the patient's pain severity, medical history, and response to treatment. The usual starting dose is 2.5-5mg orally every 4-6 hours, with adjustments made as needed.
- Titration: Morphine doses should be titrated gradually to minimize the risk of respiratory depression and other side effects.
- Monitoring: Patients receiving morphine should be closely monitored for signs of respiratory depression, including decreased respiratory rate, shallow breathing, and oxygen saturation.
- Route of administration: Morphine can be administered orally, intravenously, or epidurally. The choice of route depends on the patient's specific needs and medical condition.
Side Effects of Morphine Medication
While morphine can be an effective pain management tool, it can also cause a range of side effects, including:
- Respiratory depression
- Drowsiness and sedation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Itching and pruritus
Morphine Medication Interactions

Morphine can interact with a range of medications, including:
- Benzodiazepines: Concurrent use of benzodiazepines and morphine can increase the risk of respiratory depression and sedation.
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) can interact with morphine, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Muscle relaxants: Concurrent use of muscle relaxants and morphine can increase the risk of respiratory depression and sedation.
Contraindications to Morphine Medication
Morphine is contraindicated in patients with:
- Respiratory depression: Morphine can worsen respiratory depression in patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Acute asthma: Morphine can worsen asthma symptoms in patients with acute asthma.
- Gastrointestinal obstruction: Morphine can worsen gastrointestinal obstruction in patients with pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions.
Gallery of Morphine Medication






Conclusion
Morphine medication can be a safe and effective tool for pain management when administered correctly. However, its potential for addiction and respiratory depression requires careful attention to dosing and administration. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, healthcare providers can minimize the risks associated with morphine medication and provide optimal pain management for their patients.
What is morphine medication used for?
+Morphine medication is used to manage moderate to severe pain, including acute pain, chronic pain, and palliative care.
What are the side effects of morphine medication?
+The side effects of morphine medication include respiratory depression, drowsiness and sedation, nausea and vomiting, constipation, and itching and pruritus.
Can morphine medication be used with other medications?
+Morphine medication can interact with a range of medications, including benzodiazepines, antidepressants, and muscle relaxants. Concurrent use of these medications should be approached with caution.