Bipolar disorder is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition that can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, relationships, and overall well-being. Despite its prevalence, bipolar disorder remains poorly understood, and many people struggle to recognize its symptoms and understand its effects.
Living with bipolar disorder can be a challenging and unpredictable experience. The condition is characterized by extreme mood swings, which can range from manic highs to depressive lows. These episodes can be severe and disrupt daily life, making it difficult for individuals to maintain relationships, work, and engage in everyday activities.
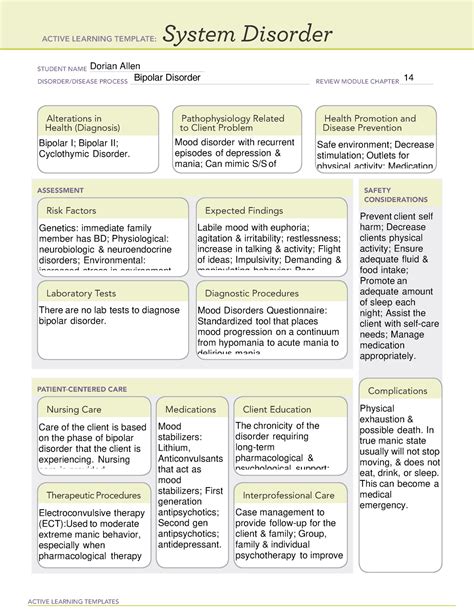
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition that affects the brain's ability to regulate mood, energy, and activity levels. It is also known as manic-depressive illness, and it is characterized by recurring episodes of mania or hypomania, often accompanied by depressive episodes.
There are several types of bipolar disorder, including:
-
Bipolar I Disorder
+ Characterized by one or more manic episodes, which may be accompanied by depressive episodes. -
Bipolar II Disorder
+ Characterized by at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode. -
Cyclothymic Disorder
+ Characterized by periods of hypomanic symptoms that last for at least two years; however, the symptoms do not meet the diagnostic requirements for a hypomanic episode.

Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes of bipolar disorder are still not fully understood, research suggests that it is linked to a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurochemical factors.
-
Genetic Factors
+ Individuals with a family history of bipolar disorder are more likely to develop the condition. -
Environmental Factors
+ Traumatic events, stress, and substance abuse can trigger episodes of mania or depression. -
Neurochemical Factors
+ Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to the development of bipolar disorder.
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
The symptoms of bipolar disorder can vary widely, depending on the type of episode and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms include:
-
Manic Symptoms
+ Increased energy and activity levels + Reduced need for sleep + Increased talkativeness and distractibility + Impulsive behavior -
Depressive Symptoms
+ Persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness + Loss of interest in activities + Changes in appetite and sleep patterns + Fatigue and decreased energy levels

Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing bipolar disorder can be a complex process, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other mental health conditions. A comprehensive diagnosis typically involves:
-
Clinical Evaluation
+ A thorough medical and mental health history + A physical examination + Laboratory tests to rule out other conditions -
Psychological Evaluation
+ A comprehensive psychological assessment + Questionnaires and rating scales to evaluate symptoms
Treatment for bipolar disorder typically involves a combination of medication and therapy. Medications can help stabilize mood and reduce symptoms, while therapy can help individuals develop coping skills and manage their condition.
-
Mood Stabilizers
+ Medications that help stabilize mood and reduce symptoms -
Antipsychotics
+ Medications that can help reduce symptoms of mania or psychosis -
Therapy
+ Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) + Interpersonal therapy (IPT) + Family-focused therapy (FFT)






Conclusion
Bipolar disorder is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the causes and symptoms can vary widely, diagnosis and treatment typically involve a combination of medication and therapy. By understanding the complexities of bipolar disorder, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their overall quality of life.
If you or someone you know is struggling with bipolar disorder, it is essential to seek professional help. With the right treatment and support, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and live a fulfilling life.
What is the difference between bipolar I and bipolar II disorder?
+Bipolar I disorder is characterized by one or more manic episodes, which may be accompanied by depressive episodes. Bipolar II disorder is characterized by at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode.
What are the symptoms of a manic episode?
+The symptoms of a manic episode include increased energy and activity levels, reduced need for sleep, increased talkativeness and distractibility, and impulsive behavior.
How is bipolar disorder treated?
+Treatment for bipolar disorder typically involves a combination of medication and therapy. Medications can help stabilize mood and reduce symptoms, while therapy can help individuals develop coping skills and manage their condition.