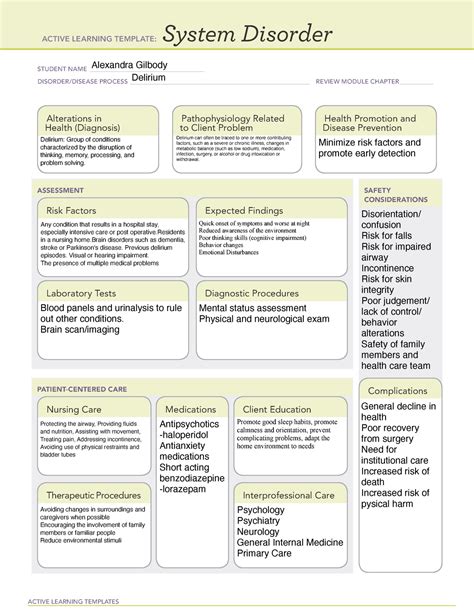
Delirium is a serious medical condition characterized by a sudden onset of confusion, altered consciousness, and disorganized thinking. It is a common problem in hospitals, affecting up to 50% of elderly patients and 80% of those in intensive care units. Delirium can be caused by a variety of factors, including medication, infection, surgery, and underlying medical conditions. In this article, we will discuss the diagnosis and treatment of delirium, as well as strategies for prevention and management.
Understanding Delirium

Delirium is a complex condition that can manifest in different ways. It is often characterized by:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Altered level of consciousness
- Disorganized thinking and speech
- Memory problems
- Difficulty with attention and concentration
- Sleep disturbances
- Emotional changes, such as anxiety, agitation, or depression
Delirium can be hyperactive, hypoactive, or mixed. Hyperactive delirium is characterized by agitation, restlessness, and aggressive behavior. Hypoactive delirium is marked by lethargy, decreased responsiveness, and a lack of initiative. Mixed delirium combines features of both hyperactive and hypoactive delirium.
Causes of Delirium
Delirium can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Medications, such as sedatives, antidepressants, and antihistamines
- Infections, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis
- Surgery, particularly in elderly patients or those with underlying medical conditions
- Underlying medical conditions, such as dementia, Parkinson's disease, and stroke
- Sleep disturbances, such as sleep apnea and insomnia
- Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Substance abuse and withdrawal
Diagnosing Delirium

Diagnosing delirium requires a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and behavioral observations. The following tools can help diagnose delirium:
- Confusion Assessment Method (CAM)
- Delirium Rating Scale (DRS)
- Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
- Clinical Assessment of Confusion (CAC)
A diagnosis of delirium is typically made when a patient exhibits a sudden onset of confusion, altered consciousness, and disorganized thinking, along with at least one of the following:
- Difficulty with attention and concentration
- Memory problems
- Disorganized thinking and speech
- Sleep disturbances
- Emotional changes
Treatment of Delirium
The treatment of delirium involves a combination of non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions. The primary goal of treatment is to address the underlying cause of delirium and manage symptoms.
Non-pharmacological interventions include:
- Environmental changes, such as reducing noise and increasing lighting
- Orientation techniques, such as providing calendars and clocks
- Sleep promotion strategies, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule
- Pain management
- Nutrition and hydration support
Pharmacological interventions may include:
- Antipsychotics, such as haloperidol and risperidone
- Benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam and midazolam
- Anticonvulsants, such as valproate and carbamazepine
- Cholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil and rivastigmine
Prevention and Management of Delirium

Preventing delirium requires a proactive approach that addresses the underlying causes of the condition. Strategies for prevention include:
- Identifying high-risk patients
- Implementing non-pharmacological interventions
- Avoiding medications that can contribute to delirium
- Managing pain and sleep disturbances
- Promoting nutrition and hydration
Managing delirium requires a comprehensive approach that involves:
- Monitoring the patient's condition closely
- Adjusting treatment plans as needed
- Providing education and support to family members and caregivers
- Encouraging patient participation in care
Gallery of Delirium-Related Images






Frequently Asked Questions
What is delirium?
+Delirium is a serious medical condition characterized by a sudden onset of confusion, altered consciousness, and disorganized thinking.
What are the causes of delirium?
+Delirium can be caused by a variety of factors, including medications, infections, surgery, underlying medical conditions, sleep disturbances, and substance abuse.
How is delirium diagnosed?
+Delirium is diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and behavioral observations.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of delirium, its causes, diagnosis, treatment, and management. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of delirium, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Remember, prevention and early intervention are key to managing this condition.