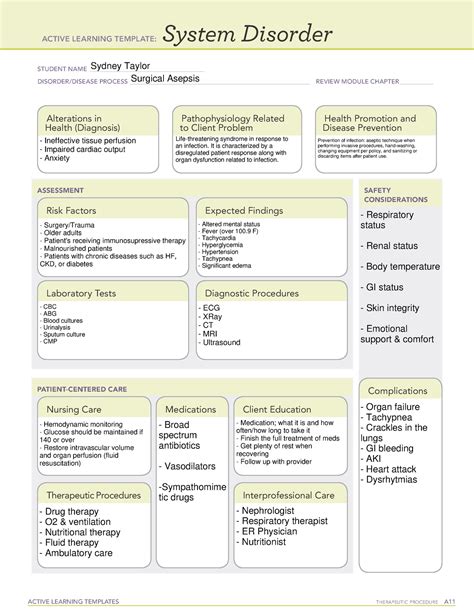
Maintaining a sterile environment is crucial in medical and surgical settings to prevent the spread of infections and ensure patient safety. Asepsis, the state of being free from disease-causing microorganisms, is a fundamental principle in healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the world of medical and surgical asepsis, exploring its importance, techniques, and best practices.
The Importance of Asepsis in Healthcare
Asepsis is a critical aspect of healthcare that plays a vital role in preventing hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). HAIs are a significant concern in healthcare settings, affecting millions of patients worldwide each year. These infections can lead to prolonged hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and even death. By maintaining a sterile environment, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of HAIs and promote patient safety.

Techniques of Asepsis
There are several techniques used to maintain asepsis in medical and surgical settings. These include:
- Hand Hygiene: Hand hygiene is the most critical aspect of asepsis. Healthcare professionals must wash their hands frequently with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, is used to prevent the transmission of microorganisms.
- Sterilization: Sterilization is the process of destroying all microorganisms on an object or surface. This is typically achieved through the use of autoclaves, dry heat sterilizers, or chemical sterilizers.
- Disinfection: Disinfection is the process of reducing the number of microorganisms on an object or surface. This is typically achieved through the use of disinfectants.

Principles of Surgical Asepsis
Surgical asepsis is a critical aspect of patient care in the operating room. The following principles are essential to maintaining asepsis during surgical procedures:
- Preparation of the Surgical Site: The surgical site must be prepared by cleaning and disinfecting the skin.
- Use of Sterile Equipment: All equipment used during surgery must be sterile.
- Maintenance of a Sterile Field: A sterile field must be maintained throughout the procedure.
- Minimizing Traffic in the Operating Room: Traffic in the operating room must be minimized to prevent contamination.

ATI Template and Guide
The ATI template and guide is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals seeking to improve their knowledge and skills in medical and surgical asepsis. The template and guide provide a comprehensive overview of asepsis principles and techniques, as well as best practices for maintaining a sterile environment.

Best Practices for Maintaining Asepsis
Maintaining asepsis requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and best practices. The following are some best practices for maintaining asepsis in medical and surgical settings:
- Use of Checklists: Checklists can be used to ensure that all necessary steps are taken to maintain asepsis.
- Regular Audits: Regular audits can be used to ensure that asepsis policies and procedures are being followed.
- Education and Training: Education and training are critical to ensuring that healthcare professionals have the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain asepsis.
- Use of Technology: Technology, such as automated dispensers and ultraviolet light disinfection, can be used to improve asepsis.

Gallery of Asepsis and Sterilization






FAQs
What is asepsis?
+Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing microorganisms.
Why is asepsis important in healthcare?
+Asepsis is critical in healthcare as it prevents the spread of infections and ensures patient safety.
What are some techniques used to maintain asepsis?
+Techniques used to maintain asepsis include hand hygiene, personal protective equipment, sterilization, and disinfection.
In conclusion, maintaining asepsis is crucial in medical and surgical settings to prevent the spread of infections and ensure patient safety. By understanding the principles and techniques of asepsis, healthcare professionals can play a critical role in promoting patient safety and preventing HAIs.