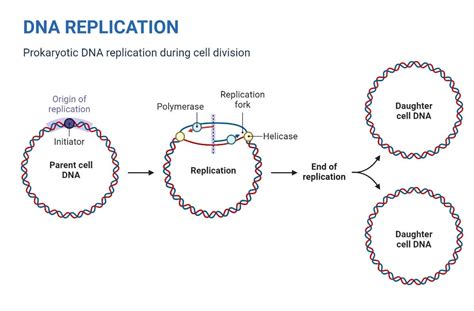
The discovery of DNA's double helix structure in 1953 revolutionized the field of molecular biology. One of the most significant implications of this discovery was the understanding of how DNA replicates itself. Semiconservative replication is the process by which DNA makes an exact copy of itself, ensuring that genetic information is passed on to the next generation. At the heart of this process is the template role, where the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What is Semiconservative Replication?
Semiconservative replication is a type of DNA replication where the original DNA molecule is used as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand. This process is "semiconservative" because the resulting DNA molecule is composed of one old strand (the template) and one new strand (the complementary strand). This is in contrast to conservative replication, where the original DNA molecule is preserved intact, and liberal replication, where the original DNA molecule is completely replaced.
Key Features of Semiconservative Replication
Semiconservative replication involves several key features that ensure the accurate copying of genetic information:
- Template-directed synthesis: The original DNA molecule serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
- Base pairing: The new strand is synthesized by pairing nucleotides with the corresponding bases on the template strand (A-T and G-C).
- Processivity: DNA replication is a continuous process, with the replication machinery moving along the template strand and synthesizing the new strand.
- Fidelity: The replication process is highly accurate, with an error rate of less than 1 in 10^6 nucleotides.
The Template Role in Semiconservative Replication
The template role is crucial in semiconservative replication, as it provides the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The template strand is unwound, and the replication machinery reads the base sequence and matches nucleotides to the corresponding bases.
Key Steps in the Template Role
The template role involves several key steps:
- Unwinding: The double helix is unwound, and the replication machinery reads the base sequence.
- Base pairing: Nucleotides are matched to the corresponding bases on the template strand.
- Synthesis: The new strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the growing chain.
- Proofreading: The replication machinery checks for errors and corrects them.
Benefits of Semiconservative Replication
Semiconservative replication provides several benefits, including:
- Genetic stability: The template role ensures that genetic information is accurately copied and preserved.
- High fidelity: The replication process is highly accurate, reducing the risk of mutations.
- Efficient: Semiconservative replication is a rapid and efficient process, allowing cells to quickly replicate their DNA.
Challenges and Limitations
While semiconservative replication is a highly efficient and accurate process, there are challenges and limitations, including:
- Error correction: The replication machinery can make mistakes, which can lead to mutations.
- DNA damage: The template strand can be damaged, which can affect the accuracy of replication.
- Evolutionary constraints: Semiconservative replication can limit the rate of evolution, as changes to the genome are more difficult to introduce.
Conclusion
Semiconservative replication is a critical process that ensures the accurate copying of genetic information. The template role is central to this process, providing the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. Understanding the mechanisms of semiconservative replication has significant implications for our understanding of genetics, evolution, and disease.

What is semiconservative replication?
+Semiconservative replication is a type of DNA replication where the original DNA molecule is used as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand.
What is the template role in semiconservative replication?
+The template role is central to semiconservative replication, providing the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What are the benefits of semiconservative replication?
+The benefits of semiconservative replication include genetic stability, high fidelity, and efficient replication.