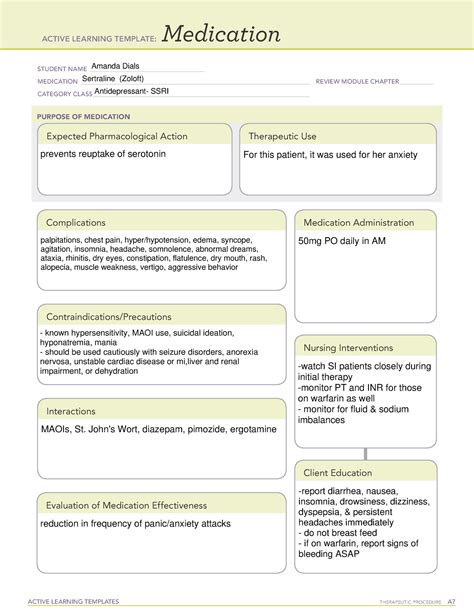
The Importance of Understanding Sertraline Medication
Sertraline, a commonly prescribed medication, is widely used to treat various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). With its popularity, it's essential to understand the ins and outs of sertraline, its uses, benefits, potential side effects, and interactions. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of sertraline, helping patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals navigate its complexities.
The History and Development of Sertraline
Sertraline, also known by its brand name Zoloft, was first introduced in the late 1980s by Pfizer. It belongs to a class of medications called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep, among other functions. By inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, sertraline allows more of this neurotransmitter to be available in the brain, thereby alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Uses of Sertraline
Sertraline is primarily used to treat a range of mental health conditions, including:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Panic disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Social anxiety disorder
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
In addition to these conditions, sertraline may also be prescribed off-label for other purposes, such as treating eating disorders, migraines, or fibromyalgia.

How Sertraline Works
Sertraline works by selectively inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, allowing more of this neurotransmitter to be available in the brain. This increase in serotonin levels helps to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. The exact mechanism of sertraline's action is complex and involves multiple neurotransmitter systems, but it's thought to involve the following processes:
- Inhibition of serotonin reuptake
- Increased serotonin release
- Modulation of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine
Benefits of Sertraline
Sertraline has several benefits that make it a popular treatment option for mental health conditions. Some of the advantages of sertraline include:
- Efficacy in treating a range of mental health conditions
- Relatively fast onset of action, with some patients experiencing improvements in symptoms within 1-2 weeks
- Generally well-tolerated, with a low risk of serious side effects
- Available in a range of formulations, including tablets, oral solution, and capsules
Potential Side Effects of Sertraline
While sertraline is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, especially during the initial treatment period. Common side effects of sertraline include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Increased sweating
Serious side effects of sertraline are rare but can include:
- Serotonin syndrome
- Increased risk of bleeding
- Seizures
- Allergic reactions
Interactions with Other Medications
Sertraline can interact with other medications, including:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Other SSRIs
- Blood thinners
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you're taking to minimize the risk of interactions.

Dosage and Administration
The dosage of sertraline varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient's needs. Typical dosages of sertraline include:
- 25-200 mg per day for MDD
- 50-200 mg per day for OCD
- 25-100 mg per day for panic disorder
Sertraline is usually taken once daily, with or without food.
What to Expect When Taking Sertraline
When taking sertraline, it's essential to be aware of the following:
- Initial treatment period: It may take 1-2 weeks to experience improvements in symptoms.
- Dose adjustments: Your healthcare provider may adjust your dosage to achieve optimal results.
- Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of your symptoms and side effects is crucial to ensure safe and effective treatment.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Stopping sertraline abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as dizziness and headaches.






Conclusion
Sertraline is a widely used medication for treating mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and OCD. By understanding its uses, benefits, potential side effects, and interactions, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to achieve optimal results. If you have any questions or concerns about sertraline, don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
What is sertraline used for?
+Sertraline is used to treat various mental health conditions, including major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, social anxiety disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
How long does it take for sertraline to work?
+It may take 1-2 weeks to experience improvements in symptoms when taking sertraline.
What are the common side effects of sertraline?
+Common side effects of sertraline include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, fatigue, insomnia, and increased sweating.