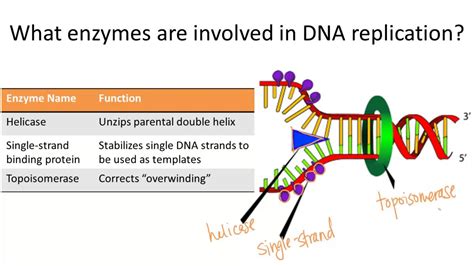
DNA unwinding is a crucial process in the replication and transcription of genetic material. It involves the separation of the two strands of DNA, allowing enzymes to access the genetic code and initiate replication or transcription. However, this process requires energy, which is provided by the molecule ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). In this article, we will explore the role of ATP in DNA unwinding and the enzymes involved in this process.
Understanding DNA Unwinding
DNA unwinding is a complex process that involves the separation of the two strands of DNA. This process is essential for the replication and transcription of genetic material, as it allows enzymes to access the genetic code and initiate replication or transcription. However, DNA unwinding is an energy-requiring process, as the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds.

The Role of ATP in DNA Unwinding
ATP is a molecule that provides energy for various cellular processes, including DNA unwinding. During DNA unwinding, ATP is hydrolyzed to release energy, which is then used to separate the two strands of DNA. This process is catalyzed by enzymes called helicases, which are responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix.
Helicases: The Enzymes Responsible for DNA Unwinding
Helicases are a class of enzymes that play a crucial role in DNA unwinding. These enzymes use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to separate the two strands of DNA, allowing other enzymes to access the genetic code and initiate replication or transcription. There are several types of helicases, each with distinct properties and functions.
Types of Helicases
There are several types of helicases, including:
- DNA helicases: These enzymes are responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication and transcription.
- RNA helicases: These enzymes are responsible for unwinding the RNA double helix during translation.
- DNA/RNA helicases: These enzymes can unwind both DNA and RNA double helices.
The Mechanism of Helicase-Mediated DNA Unwinding
The mechanism of helicase-mediated DNA unwinding involves the following steps:
- Binding of helicase to DNA: The helicase enzyme binds to the DNA double helix, positioning itself at the replication fork.
- Hydrolysis of ATP: The helicase enzyme hydrolyzes ATP to release energy, which is then used to unwind the DNA double helix.
- Unwinding of DNA: The helicase enzyme uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to separate the two strands of DNA, creating a replication fork.
- Synthesis of new DNA strands: Other enzymes, such as DNA polymerase, synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the template strands.

Conclusion
In conclusion, ATP plays a crucial role in DNA unwinding by providing the energy required for the separation of the two strands of DNA. Helicases are the enzymes responsible for catalyzing this process, using the energy from ATP hydrolysis to unwind the DNA double helix. Understanding the mechanism of helicase-mediated DNA unwinding is essential for appreciating the complex processes involved in the replication and transcription of genetic material.
Gallery of DNA Unwinding






What is the role of ATP in DNA unwinding?
+ATP provides the energy required for the separation of the two strands of DNA during DNA unwinding.
What are helicases?
+Helicases are enzymes that use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to unwind the DNA double helix during replication and transcription.
What is the mechanism of helicase-mediated DNA unwinding?
+The mechanism involves the binding of helicase to DNA, hydrolysis of ATP, unwinding of DNA, and synthesis of new DNA strands.